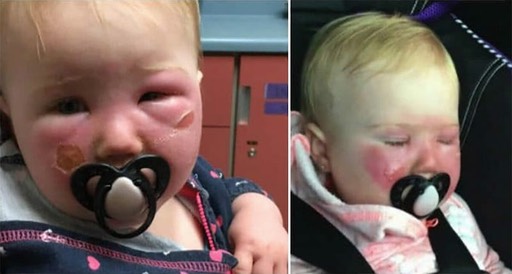
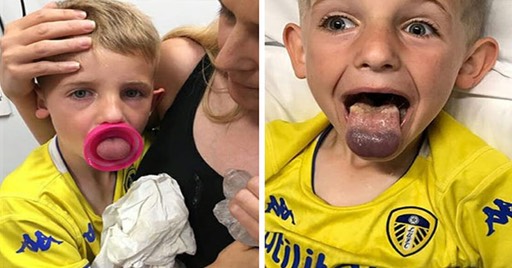
One of the most remarkable breakthroughs in medical science during the last century was the invention of vaccines to prevent a broad number of communicable diseases.
Today, virtually every child in the first world and many millions more in the developing world have simple and affordable access to these miracle drugs.
But now a relatively common disease is spreading throughout Georgia, with parents and doctors unable to do anything about it.
Commonly referred to as Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease, it is sweeping through classrooms and daycare centers in the American South. Find out what, if anything can be done to protect your children.
Year after year, parents, doctors, and school administrators have to deal with the nasty little bugs that kids transfer to each other.
Since kids are notoriously bad about hygiene and will put almost anything in their mouths, it is no wonder that daycare centers, kindergartens, and schools become breeding grounds for all sorts of awful sickness.
And now there is a new…
superbug for parents to worry about: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease. This disease affects kids all over the world and about two hundred thousand right here in the United States every year.
According to the West Central Health District in Georgia, 2017 may be a record year for this illness.
There is no vaccine against hand-foot-and-mouth disease, or HFMD for short, available in the United States, however, China began administering one in 2015.
It spreads easily through closed spaces like classrooms and dormitories, and among groups with underdeveloped immune systems and poor hygiene. It also is spread through mucous and saliva, so it is a serious problem for children, parents, and educators.
Luckily, however, HFMD is not particularly dangerous. It has some very nasty symptoms which are easily recognized, and the run of the illness is about seven to ten days.
If you are concerned about HFMD, here are some things you need to be aware of and on the lookout for:
It is not airborne but is easily transmitted in close quarters through sneezes, coughing, kissing, or handshakes. So classrooms, subway trains, buses, and hospitals are all pretty good places to catch it.
The most susceptible people include…
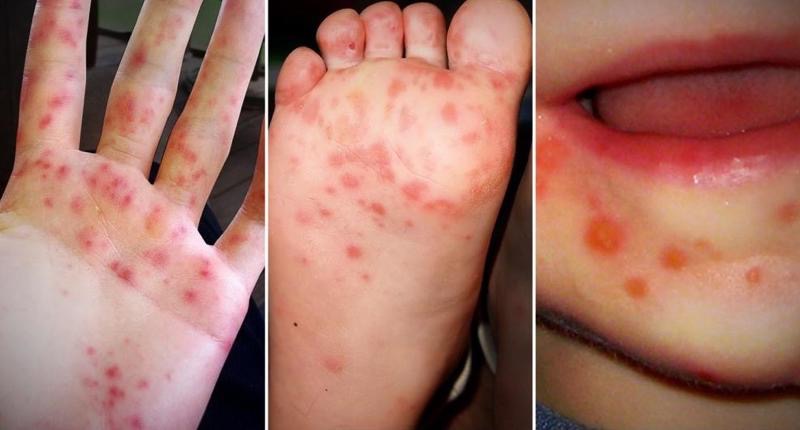
small children, college kids who are stressed and may share food or be intimate, and the elderly, especially those that live in nursing homes.
HFMD symptoms are easy to spot: Just look for the spots. These itchy red spots will appear around the mouth, palms, and soles of the feet. Sometimes they may also appear on the legs and genitals. While these outward signs may look horrific, they will usually clear up in a little over a week.
Other symptoms can closely mimic the common flu and include a sore throat, fatigue, and fever.
It is extremely contagious and there is no vaccine available in the US, nor a real course of treatment beyond isolating the patient for the period to prevent its spread.
The disease itself is fairly benign but can lead to complications for people who are in poor health, to begin with. Some include meningitis and encephalitis. Also, children whose infection takes longer than a couple of weeks to run its course, my wind up losing finger and toe nails.
The best way to prevent the spread of HFMD is to be diligent in hygiene practices and to make sure your kids are as well.
Have you ever contracted this disease? Share your experience with us here.
Watch the news report below, leave your comments and share this with your friends on social media to help others!